Problem Identification:
The Resonance Institute team visited the factory where the equipment listed below is located for a vibration measurement project:

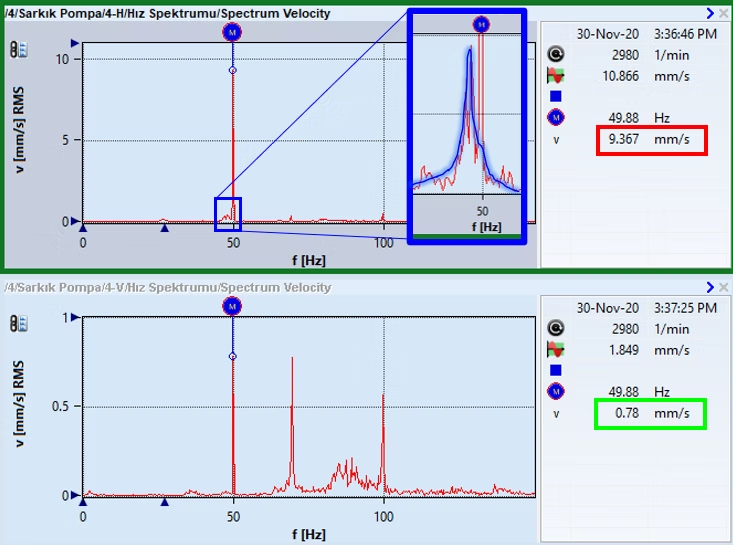
Hot rolling mill descaling pumps are critical for production, operating at a fixed speed of 3000 RPM. The variable load pump experiences excessive vibration at 1X frequency in the horizontal direction. Due to vibration levels in the vertical direction being nearly 7-8 times higher than the observed 1X vibration, failures occur every 3-4 months.
The fact that the horizontal vibration is considerably higher than the vertical vibration is one of the signs of a mechanical looseness problem. In addition, the presence of a bulge – noise floor below the 1X frequency in the velocity spectrum taken horizontally has led the analysis expert to consider a resonance problem.
Modal Test:
Based on resonance suspicion, it has been decided to perform a Modal Test measurement.
This measurement can prove the existence of a possible natural frequency condition in the machine and/or its base.
The equipment is stopped during the measurement and shaken at specific locations using a ‘modal hammer’ containing a force sensor. At this stage, vibration data is also collected simultaneously using accelerometers.
Force input is provided with the modal hammer, and vibration output is measured with accelerometers. The transfer function between them provides information related to structural dynamics (natural frequency regions, amount of damping, etc.).
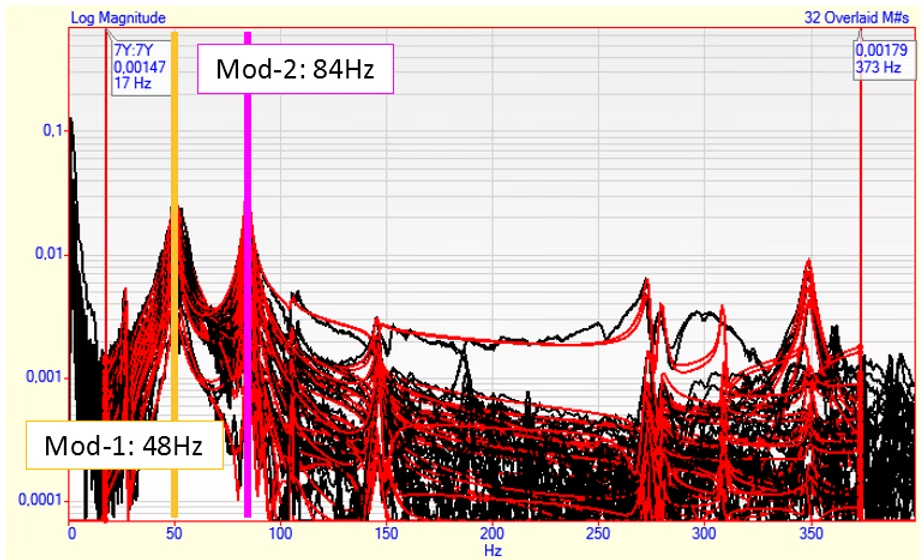
- As a result of the Modal Test study, an effective natural frequency was detected in the horizontal direction just below the 1X frequency (48Hz).
- In addition, the existence of another natural frequency effective in the 84Hz range has also been proven.
- The natural frequencies observed at 48Hz and 84Hz have been determined to be the first and second modes of the pump in the horizontal plane. The mode shapes corresponding to these modes are as shown in the animations below.
Style Types:
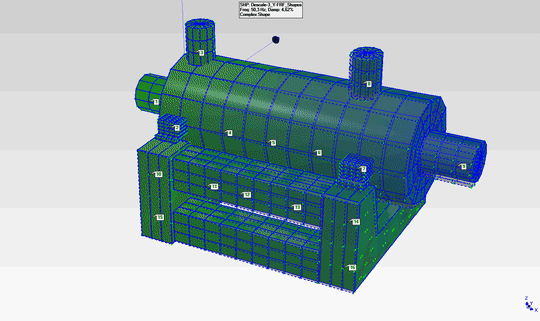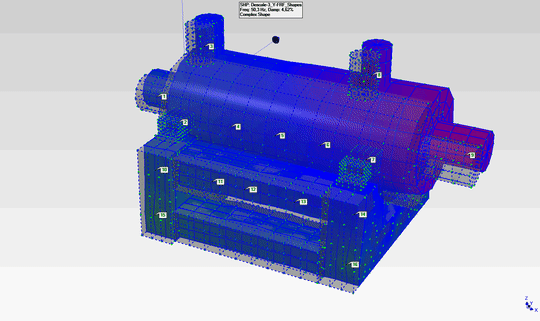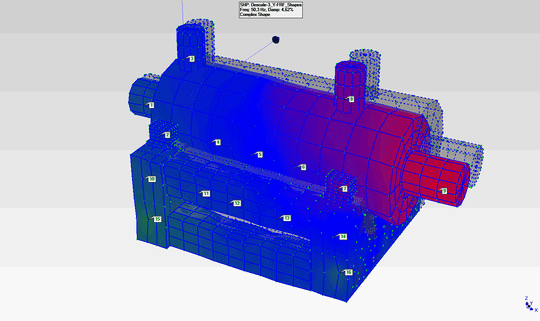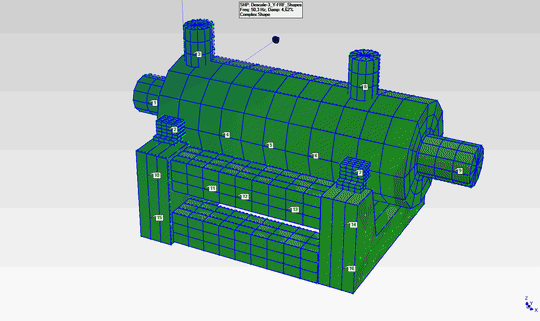
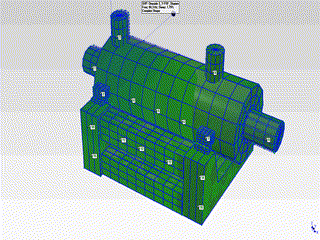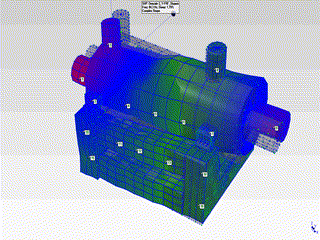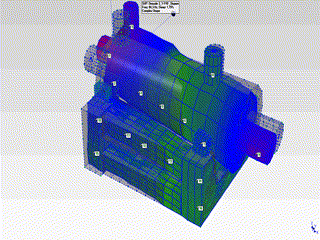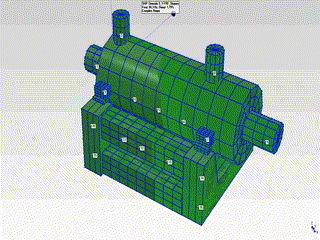
- The mode shapes for the first mode (48Hz) and second mode (84Hz) are shown on the right.
- By examining these mode shapes, it is clearly evident that, in order to shift the natural frequency regions to safer frequency ranges, horizontal support must be provided at appropriate locations.
- The proposed horizontal support work and the actual support structures are as shown below.
Corrective Actions:
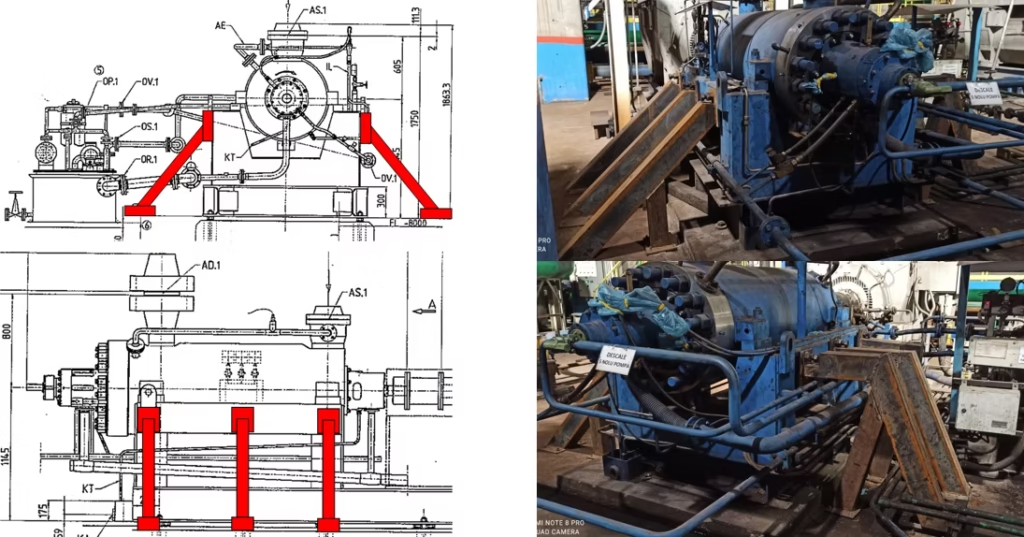
Result:
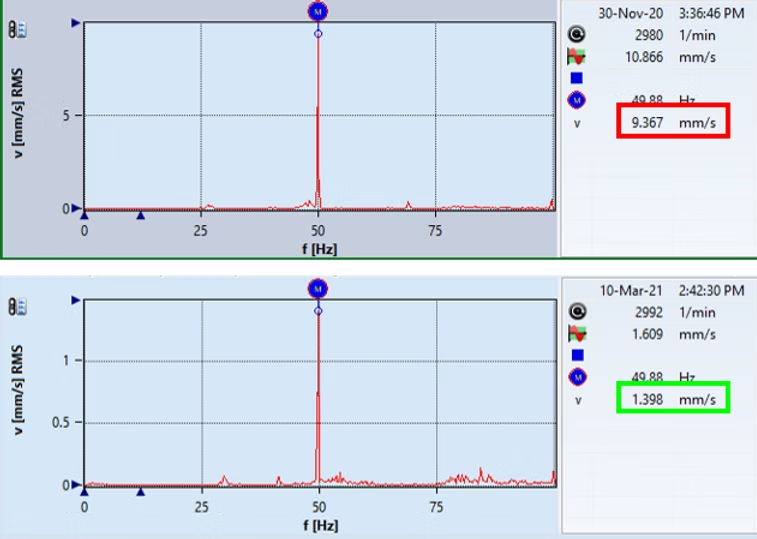
- As a result of supporting the pump horizontally, some shift has occurred in the natural frequency regions (still not sufficient) and significant reductions in vibration levels have been observed (85% improvement).
- It has been observed that the natural frequency in the 48Hz range, which affects 1X and causes resonance, shifts to 54Hz, thereby reducing vibrations to some extent.
- To prevent this situation from recurring, it has been decided to place V-rings in front of the sealing elements and to increase the gaps between the sealing elements.
- Ideally, the natural frequency should be no more than 20% away from the forced vibration frequency (in this case, above 60Hz or below 40Hz).
- Lower vibration levels dramatically reduce the likelihood of failure.
 English (İngilizce)
English (İngilizce) Türkçe (Turkish)
Türkçe (Turkish)